| Setting | Model | Item F1 Score (%) | Row F1 Score (%) | Success Rate (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avg@4 | Max@4 | Avg@4 | Max@4 | Avg@4 | Pass@4 | ||
| Single Agent |
SingleSeek-R1-4B | 28.1 | 39.2 | 6.5 | 12.5 | 0.3 | 1.0 |
| Qwen3-4B | 20.1 | 30.2 | 3.0 | 4.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| Search-R1-7B | 15.5 | 24.4 | 2.0 | 4.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| ASearcher-7B | 16.5 | 26.0 | 2.8 | 5.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| DeepSeek-R1-671B | 41.3 | 55.1 | 20.7 | 31.7 | 0.4 | 1.5 | |
| Multi-Agent System |
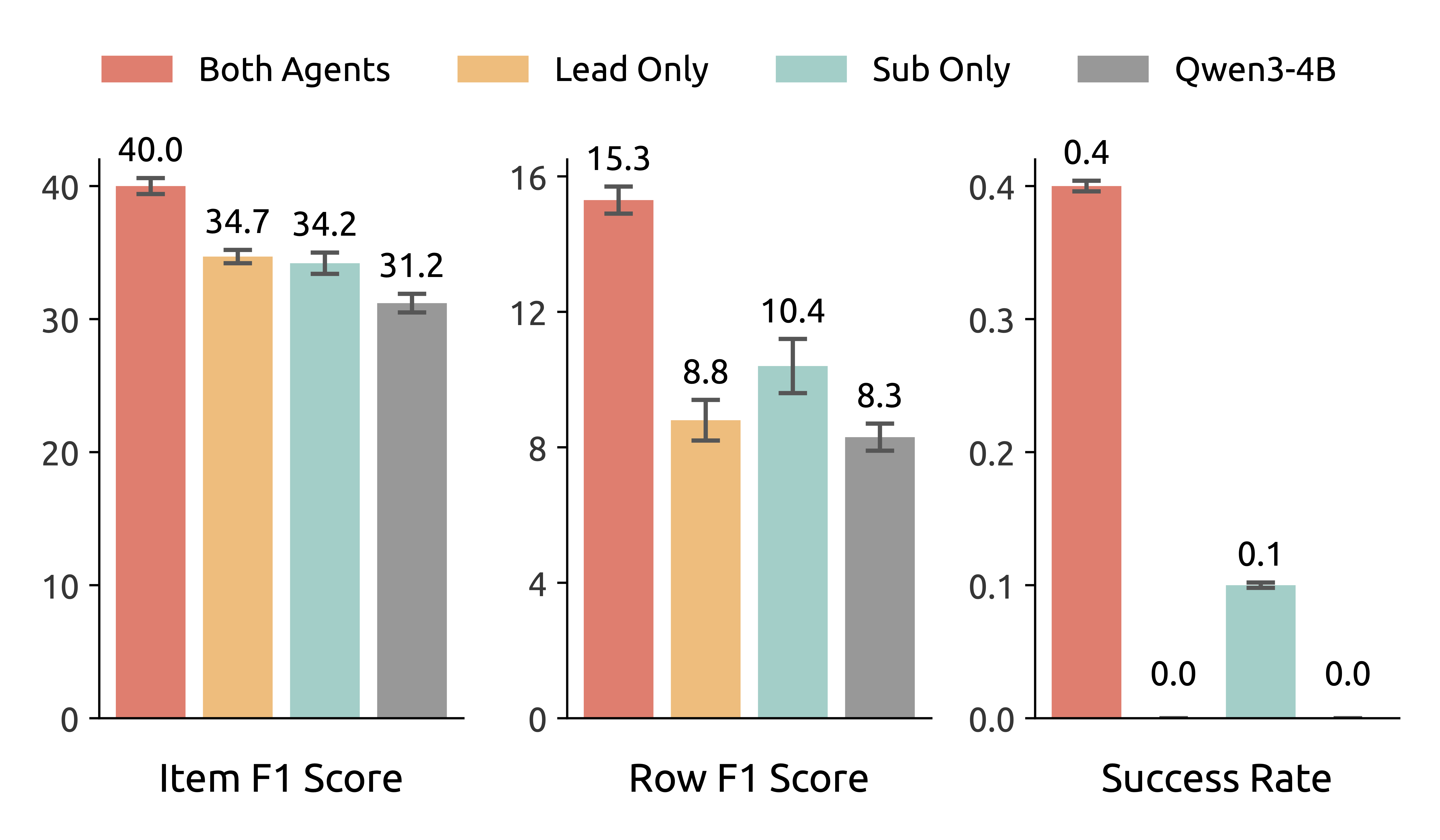
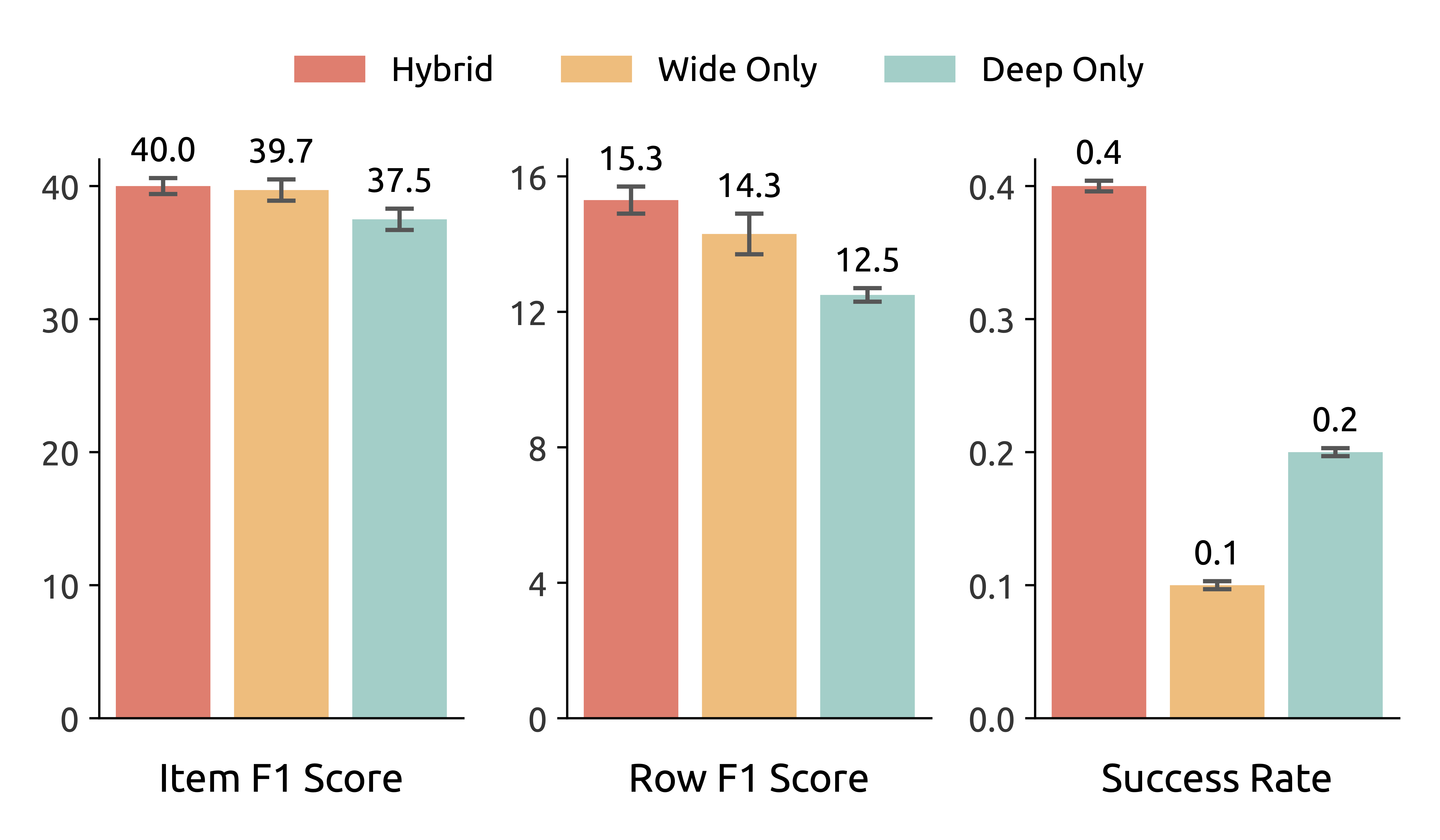
WideSeek-R1-4B | 40.0 | 51.8 | 15.3 | 24.4 | 0.4 | 1.0 |
| Qwen3-4B | 31.2 | 42.3 | 8.4 | 15.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| AgentFlow-7B | 28.7 | 45.4 | 9.0 | 20.2 | 0.4 | 1.5 | |
| OWL-8B | 20.2 | 29.3 | 3.1 | 5.8 | 0.0 | 0.0 | |
| MiroFlow-8B | 23.7 | 37.7 | 5.8 | 12.7 | 0.4 | 1.0 | |
WideSeek-R1-4B achieves performance comparable to DeepSeek-R1-671B while using nearly 170x fewer parameters.